A Comprehensive Guide to Diabetes Management
Diabetes is a chronic illness that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the body is unable to properly regulate blood sugar levels. Without effective management, diabetes can lead to serious complications such as cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage. This comprehensive guide aims to provide valuable information and strategies for effectively managing diabetes.
Understanding Diabetes
Diabetes is categorized into three main types: Type 1, Type 2, and gestational diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease where the body doesn’t produce insulin. Type 2 diabetes occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough insulin. Gestational diabetes affects pregnant women and usually disappears after childbirth.
To manage diabetes effectively, it’s crucial to have a thorough understanding of the condition. Regular blood sugar monitoring is necessary to ensure levels remain within the target range. A healthcare provider can help determine specific blood sugar targets based on individual needs and circumstances.
Healthy Eating and Meal Planning
Proper nutrition plays a vital role in diabetes management. Following a balanced diet can help regulate blood sugar levels and maintain overall health. Consuming whole foods that are high in fiber and low in added sugars is recommended. Meal planning and portion control are also essential to prevent blood sugar spikes.
Structured meal times and regularity in the consumption of carbohydrates are important factors in managing diabetes. Eating smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day can help stabilize blood sugar levels. It’s advised to consult with a registered dietitian for personalized meal planning guidance.
Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is beneficial for individuals with diabetes. Engaging in moderate-intensity exercises, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming, helps improve insulin sensitivity and can lead to better blood sugar control. It’s essential to choose activities that are enjoyable and sustainable to ensure long-term adherence.
Before starting any new exercise program, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional to ensure it is safe and suitable for the individual’s condition. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels before, during, and after exercise helps determine the impact of physical activity on blood glucose.
Medication and Insulin Therapy
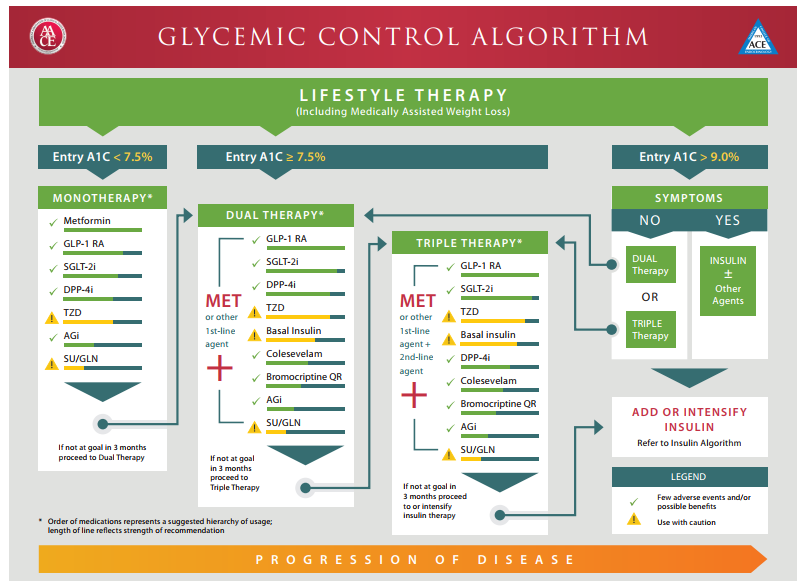
In addition to lifestyle changes, many individuals with diabetes require medication or insulin therapy to manage their condition. The type and dosage of medication prescribed by healthcare professionals can vary depending on the type of diabetes, individual needs, and other health factors.
Strict adherence to medication and insulin therapy schedules is crucial for effective diabetes management. It’s important to consult a healthcare provider for guidance on the correct administration and potential side effects of medications or insulin.
Stress Management and Emotional Well-being
Stress can adversely affect blood sugar control in individuals with diabetes. Finding healthy coping mechanisms and stress management techniques is important for overall well-being. Engaging in activities like mindfulness meditation, yoga, or pursuing hobbies can help reduce stress levels.
Emotional support from friends, family, and support groups can make a significant difference in diabetes management. Sharing experiences, concerns, and successes with others who understand the challenges of living with diabetes can provide valuable emotional support and encouragement.
Regular Check-ups and Self-monitoring
Regular check-ups with healthcare professionals are essential for monitoring diabetes and preventing complications. These appointments may involve blood sugar level evaluations, A1C tests, blood pressure checks, and cholesterol screenings. These tests help healthcare providers assess overall diabetes management and make any necessary adjustments.
Self-monitoring of blood sugar levels using advanced glucometers is an important aspect of diabetes management. Keeping a log of blood sugar readings, medication dosages, and symptoms can help identify patterns and inform healthcare professionals to make informed decisions about treatment plans.
Diabetes Education and Support
Educating oneself about diabetes is crucial for effective management. Attend diabetes education classes or workshops to learn more about the condition, treatment options, self-care practices, and the latest research. It’s important to stay informed about new developments and advancements in diabetes management.
Additionally, joining support groups and online communities can provide a network of individuals facing similar challenges. Sharing experiences, tips, and guidance can help individuals cope with the demands of managing diabetes and provide emotional support.
Conclusion
Diabetes management requires a comprehensive approach involving lifestyle changes, proper nutrition, regular physical activity, medication or insulin therapy, stress management, and regular check-ups. By incorporating these strategies into their daily lives, individuals with diabetes can maximize their overall health and well-being, minimize the risk of complications, and effectively manage their condition.